The name Ferrous comes from the Latin word Iron “Ferrum”.
Ferrous metals are those that contain iron as the base metal, or in other words those metals which are attracted by magnets. The properties of ferrous metals may be changed by adding various alloying elements. The chemical and mechanical properties need to be combined to produce a metal to serve a specific purpose. The basic ferrous metal form is pig iron. Pig iron is produced in a blast furnace that is charged with an iron ore, coke, and limestone. Ferrous metals had a tremendous impact on lifestyle, it was one of the most important changes for mankind today Ferrous metals are the backbone of the world with built.
Ferrous metal’s ore is readily available, constituting about 5% of the earth's crust, and is easy to convert to a useful form.
The four principal iron ores are hematite, limonite, magnetite and faconite.
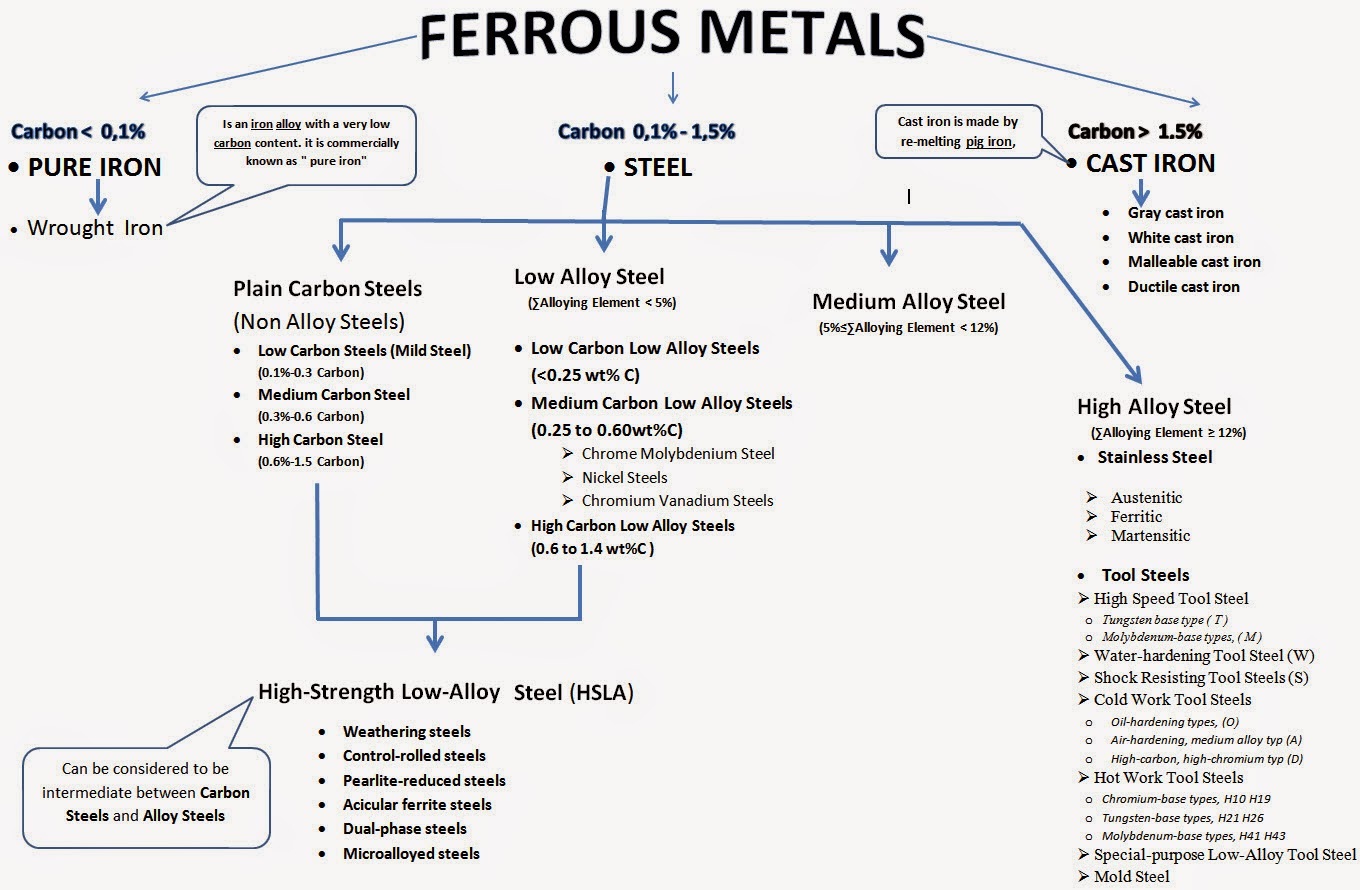
Ferrous metals include cast iron, steel, and the various steel alloys, The only difference between iron and steel is the carbon content. Cast iron contains more than 2-percent carbon, while steel contains less than 2 percent. An alloy is a substance composed of two or more elements. Therefore, all steels are an alloy of iron and carbon, but the term “alloy steel” normally refers to a steel that also contains one or more other elements. For example, if the main alloying element is tungsten, the steel is a “tungsten steel” or “tungsten alloy.” If there is no alloying material, it is a “carbon steel.”
Manipulation of atom-to-atom relationships between iron, carbon and various alloying elements establishes the specific properties of ferrous metals.
The following are ferrous metals and the kind of uses to which they are usually put:
Ferrous metals include:-
CARBON CONTENT
The Low-Carbon(Mild) Steel is soft and easily scratched the High-Carbon is much harder so High-Carbon Steel can cut Low-Carbon Steel
The cast iron with carbon content of less than 0.2% is called wrought iron or pure iron. Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content. It is commercially known as " pure iron"
The cast iron with carbon content of 0.2-1.7% is called cast steel. So, cast steel is a kind of special cast iron. More than 2% of content is called pig iron. Wrought iron is very soft, plastic and easily deformed, but its strength and hardness are lower, so not widely used.
SOME FERROUS METALS AND THEIR PROPERTIES
| NAME | ALLOY OF | PROPERTIES | USES |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel | Carbon 0.1 -0.3% Iron 99.9 - 99.7% | Tough. High tensile strength. Can be case hardened. Rusts very easily. | Most common metal used in school workshops. Used in general metal products and engineering. |
| Carbon Steel | Carbon 0.6 - 1.4% Iron 99.4 - 98.6% | Tough. Can be hardened and tempered. | Cutting tools such as drills |
| Stainless Steel | Iron, nickel and chromium | Tough, resistant to rust and stains. | Cutlery, medical instruments. |
| Cast Iron | Carbon 2 - 6% Iron 98 - 94% | Strong but brittle. Compressive strength very high. | Castings, manhole covers, engines. |
| Wrought Iron | Almost 100% iron | Fibrous, tough, ductile, resistant to rusting. | Ornamental gates and railings. Not in much use today. |
Ferrous scrap is scrap iron and steel. This includes scrap from old automobiles, farm equipment, household appliances, steel beams, railroad tracks, ships, and food packaging and other containers. Ferrous scrap accounts for the largest volume of metal scrapped. Ferrous scrap is classified into almost 80 grades; additionally, there are another 40 grades of railroad ferrous scrap and even more grades of alloy scrap. Metal alloys are made from a combination of two or more metals.