Recycling means to change waste materials (that would otherwise be waste into valuable resources) into new products to performs a vital social and environmental function. Recycling of a material would produce a fresh supply of the same material.
 Another form of recycling is the salvage of certain materials from complex products, either due to their intrinsic value or due to their hazardous nature. The industry has no peer in terms of conserving the world's natural resources while the various stages of the recycling process provide employment for millions of people all around the world.
Another form of recycling is the salvage of certain materials from complex products, either due to their intrinsic value or due to their hazardous nature. The industry has no peer in terms of conserving the world's natural resources while the various stages of the recycling process provide employment for millions of people all around the world.
We cannot possible continue enjoying these metals when they wreak havoc on our planet. We use the best solution i.e recycling.Industrial wastes if left unattended to can cause a lot of damage. Recycling waste products makes a great impact in the world. It helps preserve the natural environment for ourselves and our future generations. It is apparent that the more years go by, the more the need for better management of waste products. This is because as the wealth increases, people buy more products and create waste. When the population increases, it means there are more people to create more waste.
There are regulations that are in place to demand that industrial companies are recycling their wastes rather than disposing them off and damaging the environment.
 One area of recycling where economic factors are having an impact right now is the market for scrap ferrous metals. The most valuable ferrous scrap is steel, especially high grade stainless, but the key resource that affects prices is iron ore – and right now that’s heading down. Reduced demand from heavy industry, mostly in China, has depressed prices a five year low. This has a serious impact on the cost effectiveness of recycling ferrous scrap. While much of the cost of processing ore into usable iron or steel is in the energy low ore prices help offset this, especially when more exotic alloys are involved. To preserve the quality of stainless steel careful sorting is needed in the recycling process, and that takes more investment in technology.
One area of recycling where economic factors are having an impact right now is the market for scrap ferrous metals. The most valuable ferrous scrap is steel, especially high grade stainless, but the key resource that affects prices is iron ore – and right now that’s heading down. Reduced demand from heavy industry, mostly in China, has depressed prices a five year low. This has a serious impact on the cost effectiveness of recycling ferrous scrap. While much of the cost of processing ore into usable iron or steel is in the energy low ore prices help offset this, especially when more exotic alloys are involved. To preserve the quality of stainless steel careful sorting is needed in the recycling process, and that takes more investment in technology.
Recycled Materials Supply 40% of the Global Raw Material Needs. Approximately 1.6 million people worldwide are active in the recycling industry.
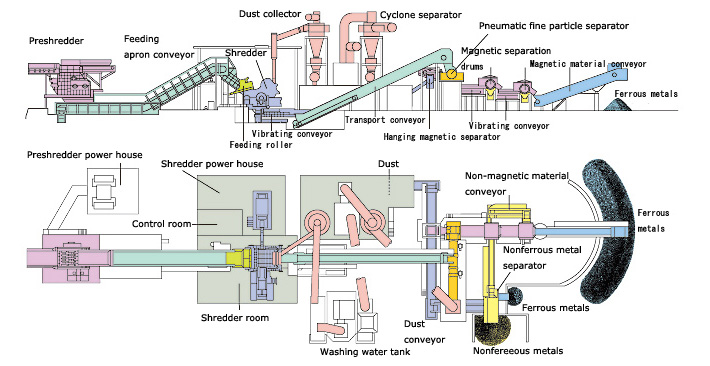
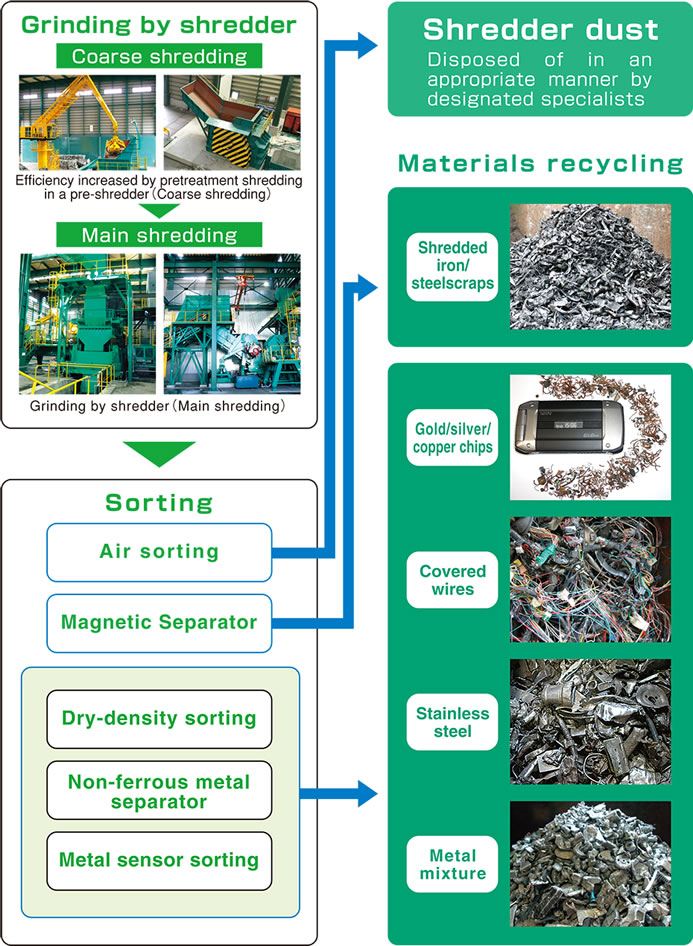
Shredder Plant (Automatic Crushing and Sorting Equipment):- Bulk waste such as scrap cars, city garbage, old home appliances and industrial waste is first roughly-crushed by a "pre-shredder".
The crushed scrap is thrown into a "shredder" by "feeding rollers" sequentially and smoothly and then further crushed into fine sized pieces. These crashed pieces are separated into iron and non-ferrous metals & dust. The iron is recovered as it is.
The mixture of non-ferrous metals and dust are separated into non-ferrous metals and dust by an "cyclone" and a "non-ferrous metals
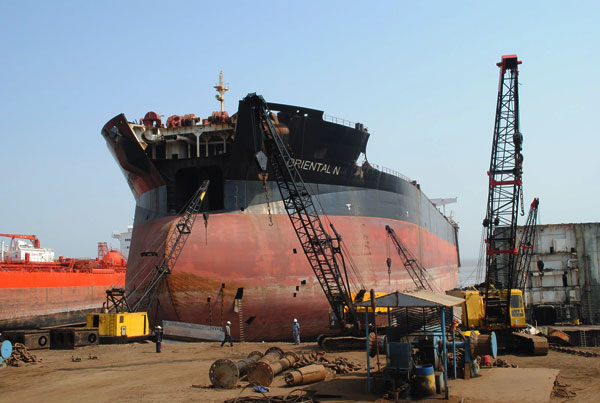 Ship breaking is a type of ship disposal involving the breaking up of ships for scrap recycling. It is the process of dismantling an obsolete vessel’s structure for scrapping or disposal. Conducted on a dismantling yard, it involves a wide range of activities. From removing all the gear and equipment that are on the ships to cutting down and recycling the ship’s infrastructure. Ship breaking is a challenging process, due to the structural complexity of the ships and the environmental, safety and health issues involved.
Due to cheaper labour costs and fewer health and safety regulations that have to be followed, the developing world hosts the vast majority of ship breaking efforts.
Ship dismantling is highly necessary as the maintenance expenses of a particular vessel keep soaring with time and it becomes really difficult to handle the same. Therefore we do the Dismantling process to overcome the problem of resources shortage and environmental issues.
Ship breaking is a type of ship disposal involving the breaking up of ships for scrap recycling. It is the process of dismantling an obsolete vessel’s structure for scrapping or disposal. Conducted on a dismantling yard, it involves a wide range of activities. From removing all the gear and equipment that are on the ships to cutting down and recycling the ship’s infrastructure. Ship breaking is a challenging process, due to the structural complexity of the ships and the environmental, safety and health issues involved.
Due to cheaper labour costs and fewer health and safety regulations that have to be followed, the developing world hosts the vast majority of ship breaking efforts.
Ship dismantling is highly necessary as the maintenance expenses of a particular vessel keep soaring with time and it becomes really difficult to handle the same. Therefore we do the Dismantling process to overcome the problem of resources shortage and environmental issues.
In general, metal recycling is a pyramid industry with many small companies at the bottom feeding scrap to large multinationals at the top. Steel recycling involves some, or , all of the following steps:
Recycling Facts: